

In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, customers expect efficient and anticipatory service. They no longer want to wait for issues to arise before receiving support; instead, they seek proactive assistance that resolves concerns before they surface. Predictive customer service, powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI), transforms how businesses engage with customers. By leveraging AI-driven insights, companies can anticipate customer needs, personalise interactions, and deliver seamless experiences that drive satisfaction and loyalty.
The Shift from Reactive to Proactive Customer Service

Traditional customer service has long been reactive, addressing issues only after customers raise concerns. While this approach has been the norm for decades, it often falls short of meeting modern consumer expectations. Customers today want businesses to understand their needs ahead of time and provide solutions proactively. For instance, McDonald’s has integrated
AI-powered systems to monitor kitchen equipment, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing operational disruptions (Wallstreet, 2025)
Predictive customer service represents a significant shift from this reactive model. It uses AI to analyse patterns, identify potential problems, and take preventive action before customers seek help. This is achieved by processing historical data, monitoring real-time interactions, and leveraging machine learning (ML) algorithms to anticipate potential customer pain points.
AI-powered predictive maintenance in industries such as telecom and IoT detects performance degradation in connected devices, triggering automated service alerts before customers experience disruptions. In e-commerce, predictive AI can detect changes in browsing behavior and offer timely customer support, reducing cart abandonment rates.
How AI Powers Predictive Customer Service

1. Data Analysis & Pattern Recognition
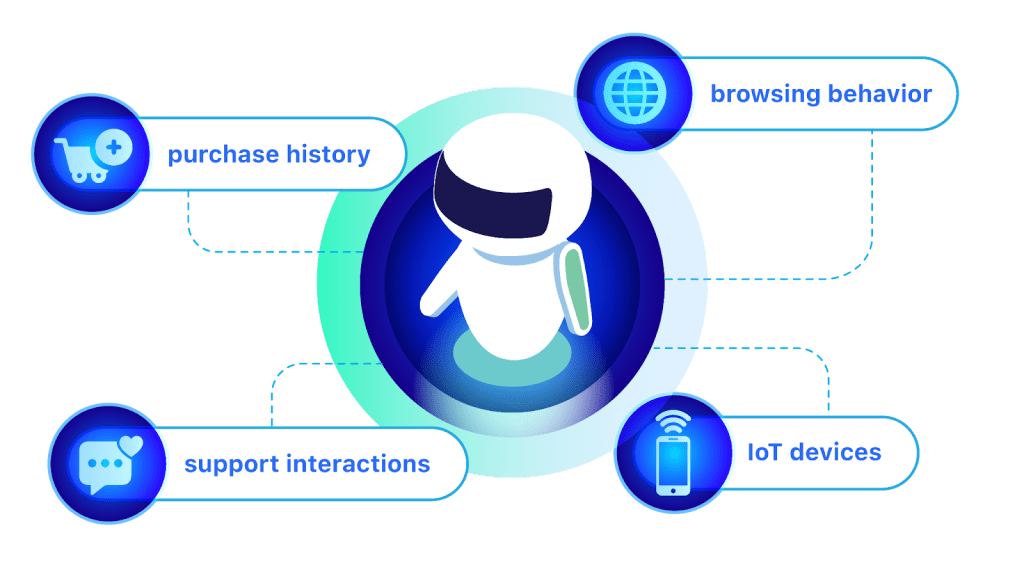
AI leverages vast customer data to anticipate needs and deliver personalised experiences. Key data sources include:
- Purchase History – Identifies patterns in buying behavior to predict future purchases and recommend relevant products.
- Browsing Behavior – Tracks interactions on websites and apps to personalise recommendations based on user interests.
- Support Interactions – Analyze previous service inquiries to anticipate future needs and improve response accuracy.
- IoT & Device Data: Internet of Things (IoT) networks generate real-time data from connected devices. Machine learning algorithms analyse this data to detect anomalies, predict maintenance needs, and enhance user experiences.
By integrating these data streams, AI-driven customer service systems can proactively address issues, improve personalisation, and optimise customer engagement.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants use NLP to understand human language, extract meaning, and provide instant, context-aware responses. Companies like Daily Harvest implement AI chatbots to improve customer service by providing rapid responses and categorising at-risk customers for personalised support (Business Insider, 2025)
Different NLP models serve distinct purposes:
- GPT-4 (Generative Model) – A transformer-based model optimised for content generation, conversational AI, and contextual responses in chatbots and virtual assistants. It excels at open-ended dialogue, summarisation, and language generation tasks.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) – An encoder-based model designed for classification tasks such as sentiment analysis, intent recognition, and named entity recognition. BERT is particularly effective in analysing customer inquiries and categorising them for more accurate and relevant responses.
By leveraging the strengths of both models, businesses can build AI-powered systems that combine conversational fluency with precise intent detection, improving customer interactions and automation.
3. Sentiment Analysis
AI assesses customer emotions by analysing language, tone, and context in customer interactions. This allows businesses to gauge satisfaction levels and intervene proactively. For instance, AI can detect frustration in chatbot conversations and escalate the issue to a human agent before the customer becomes dissatisfied.
4. Predictive Analytics & Machine Learning Models
Predictive analytics leverages machine learning models to anticipate customer behavior and improve service strategies. Some commonly used models include:
- Logistic Regression – Used for binary classification problems such as predicting customer churn likelihood based on historical data.
- Decision Trees & Random Forests – Categorize customers into risk levels for proactive engagement by analysing multiple decision factors.
- Neural Networks – Identify complex patterns in customer behavior, enabling hyper-personalization of recommendations and support strategies.
By integrating predictive analytics with CRM platforms, businesses can generate actionable insights to enhance customer retention strategies and optimise engagement efforts.
Real-World Applications of Predictive Customer Service

AI-driven predictive customer service is already transforming industries, providing tangible benefits to businesses and customers.
- Personalised Recommendations
AI suggests relevant products or services based on user behavior, improving conversion rates. Platforms like Amazon and Netflix use recommendation engines powered by collaborative filtering and deep learning models to predict customer preferences. - Proactive Issue Resolution
AI-powered predictive maintenance is widely used in the telecom, automotive, and manufacturing industries. For instance, predictive algorithms in Tesla vehicles analyse sensor data to detect potential failures and alert owners before mechanical issues arise. - AI-powered chatbots & Virtual Assistants
Businesses use AI to automate routine inquiries and deliver personalised support. Klarna’s AI assistant, for example, resolves 2.3 million customer inquiries per month and handles two-thirds of all service requests without human intervention. - Customer Churn Prevention
AI analyses engagement patterns to identify customers at risk of leaving. By integrating AI-driven insights with marketing automation platforms, businesses can send personalised offers or support messages to retain customers.
Technical Challenges and Considerations

1. Data Privacy & Security
AI relies on vast amounts of customer data, requiring businesses to comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Data encryption, anonymisation, and ethical AI practices are critical to customer trust.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
Many businesses operate on outdated CRM and ERP systems, making AI integration complex. APIs and cloud-based AI solutions, such as AWS AI Services and Google Cloud AI, help bridge this gap.
3. Balancing Automation & Human Touch
While AI enhances efficiency, over-reliance on automation can lead to impersonal interactions. Businesses must implement hybrid models where AI assists human agents rather than replacing them entirely.
4. Model Training & Bias Prevention
AI models require continuous training on diverse datasets to improve accuracy and minimize biases. Bias mitigation techniques include:
- Data Preprocessing – Ensuring balanced datasets by removing biases in training data and applying re-sampling techniques.
- Fairness-Aware Modeling – Using algorithmic approaches such as adversarial debiasing, re-weighting, and fairness constraints during model training.
- Post-processing adjustments – Calibrating model outputs to reduce bias, such as equalising false positive/negative rates across demographic groups.
By implementing these techniques, businesses can develop AI models that provide fairer and more reliable predictions, improving customer trust and satisfaction.
Implementation Strategies for AI-Powered Predictive Customer Service
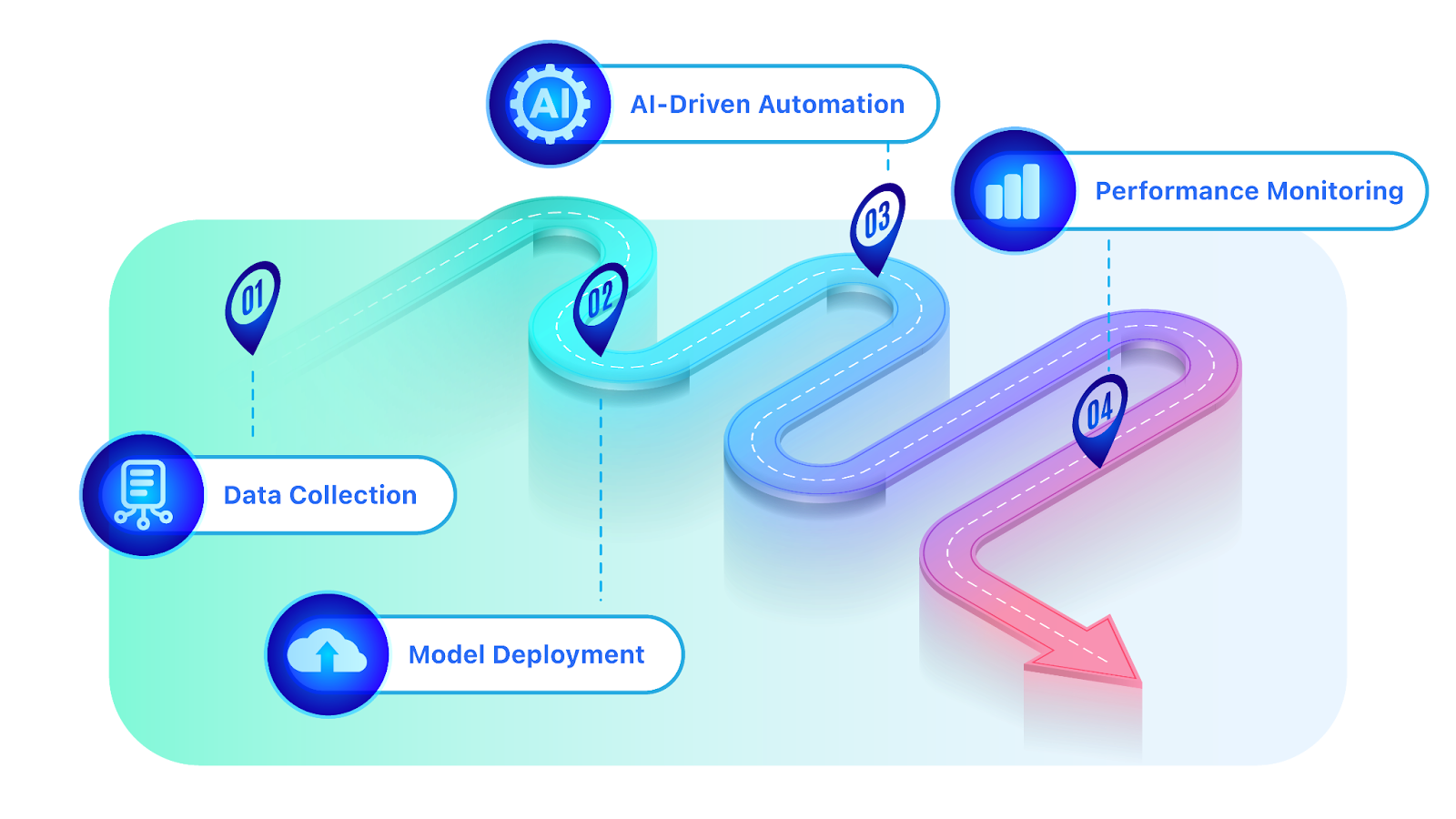
1. Data Collection & Preprocessing
- Extract and clean customer interaction logs, CRM data, and IoT telemetry.
- Use ETL pipelines (Extract, Transform, Load) to standardise data before feeding it into AI models.
2. AI Model Deployment & Integration
Choosing the right deployment approach for AI models depends on business needs, regulatory requirements, and technical constraints.
- Cloud AI Services (for Scalability & Accessibility) – Platforms like Google Cloud AI, AWS AI Services, and Microsoft Azure AI offer scalable AI infrastructure with managed services, reducing operational overhead. These are ideal for businesses needing high availability, ease of deployment, and global accessibility.
- On-Premise AI Models (for Privacy, Latency, and Compliance) – Deploying AI models on local servers or using TensorFlow, PyTorch-based custom models provide greater data security and compliance control. On-premise deployment is beneficial in scenarios requiring low latency (e.g., real-time processing), regulatory compliance (e.g., healthcare, finance), and cost control for long-term AI operations.
- Containerisation for Seamless Integration – Using Docker and Kubernetes, AI models can be packaged as portable, scalable applications that integrate seamlessly across cloud and on-premise environments. This approach ensures flexibility, allowing businesses to switch between cloud and local deployments based on their needs.
By selecting the right AI deployment strategy, businesses can optimise performance, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
3. AI-Driven Automation & Human-AI Collaboration
- AI handles routine inquiries, while humans manage complex issues.
- Escalation workflows ensure that AI refers unresolved cases to live agents.
- RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is used to automate repetitive workflows.
4. Performance Monitoring & Continuous Improvement
- Monitor AI accuracy metrics (precision, recall, F1-score).
- Use A/B testing to compare AI-driven predictions against human decisions.
- Implement AI observability tools (e.g., Weights & Biases, MLflow) to track AI performance.
The Future of Predictive Customer Service

As AI technology continues to advance, predictive customer service will evolve in the following ways:
- Hyper-Personalization – AI will integrate data from multiple sources (including social media and IoT devices) to provide highly customised experiences.
- Real-Time Adaptation – AI systems will dynamically adjust responses based on real-time customer interactions.
- Emotionally Intelligent AI – Future NLP models will better recognise and respond to human emotions, making AI-driven conversations feel more natural.
Emerging technologies such as edge AI and quantum computing are set to impact predictive customer service in specific ways:
- Edge AI – Processes data locally on devices instead of relying on cloud servers, reducing latency, conserving bandwidth, and improving privacy. This makes it particularly useful for real-time predictive services, such as chatbots on mobile devices or AI-driven fraud detection in financial transactions.
- Quantum Computing (Future Potential): While still in the research phase and not yet commercially viable, quantum computing has the potential to solve complex optimisation problems at unprecedented speeds. However, its real-world impact on customer service is still years away.
For now, businesses looking to enhance real-time predictive services should focus on edge AI deployment. At the same time, cloud-based AI models remain the most effective solution for large-scale customer service applications.
Predictive customer service is revolutionising how businesses interact with their customers. While data privacy, AI bias, and integration complexities must be addressed, the benefits far outweigh the obstacles. As AI technology advances, businesses that embrace predictive customer service will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
Book a Consultation



